Autoregressive forecasting using various Machine Learning models.
Usage
ARml(
y,
max_lag = 5,
xreg = NULL,
caret_method = "cubist",
metric = "RMSE",
pre_process = NULL,
cv = TRUE,
cv_horizon = 4,
initial_window = NULL,
fixed_window = FALSE,
verbose = TRUE,
seasonal = TRUE,
K = frequency(y)/2,
tune_grid = NULL,
lambda = NULL,
BoxCox_method = c("guerrero", "loglik"),
BoxCox_lower = -1,
BoxCox_upper = 2,
BoxCox_biasadj = FALSE,
BoxCox_fvar = NULL,
allow_parallel = FALSE,
calibrate = TRUE,
calibration_horizon = NULL,
n_cal_windows = NULL,
...
)Arguments
- y
A univariate time series object.
- max_lag
Maximum value of lag.
- xreg
Optional. A numerical vector or matrix of external regressors, which must have the same number of rows as y. (It should not be a data frame.).
- caret_method
A string specifying which classification or regression model to use. Possible values are found using names(getModelInfo()). A list of functions can also be passed for a custom model function. See https://topepo.github.io/caret/ for details.
- metric
A string that specifies what summary metric will be used to select the optimal model. See
?caret::train.- pre_process
A string vector that defines a pre-processing of the predictor data. Current possibilities are "BoxCox", "YeoJohnson", "expoTrans", "center", "scale", "range", "knnImpute", "bagImpute", "medianImpute", "pca", "ica" and "spatialSign". The default is no pre-processing. See preProcess and trainControl on the procedures and how to adjust them. Pre-processing code is only designed to work when x is a simple matrix or data frame.
- cv
Logical, if
cv = TRUEmodel selection will be done via cross-validation. Ifcv = FALSEuser need to provide a specific model viatune_gridargument.- cv_horizon
The number of consecutive values in test set sample.
- initial_window
The initial number of consecutive values in each training set sample.
- fixed_window
Logical, if FALSE, all training samples start at 1.
- verbose
A logical for printing a training log.
- seasonal
Boolean. If
seasonal = TRUEthe fourier terms will be used for modeling seasonality.- K
Maximum order(s) of Fourier terms
- tune_grid
A data frame with possible tuning values. The columns are named the same as the tuning parameters. Use getModelInfo to get a list of tuning parameters for each model or see https://topepo.github.io/caret/available-models.html. (NOTE: If given, this argument must be named.)
- lambda
BoxCox transformation parameter. If
lambda = NULLIflambda = "auto", then the transformation parameter lambda is chosen usingBoxCox.lambda.- BoxCox_method
BoxCox.lambdaargument. Choose method to be used in calculating lambda.- BoxCox_lower
BoxCox.lambdaargument. Lower limit for possible lambda values.- BoxCox_upper
BoxCox.lambdaargument. Upper limit for possible lambda values.- BoxCox_biasadj
InvBoxCoxargument. Use adjusted back-transformed mean for Box-Cox transformations. If transformed data is used to produce forecasts and fitted values, a regular back transformation will result in median forecasts. If biasadj is TRUE, an adjustment will be made to produce mean forecasts and fitted values.- BoxCox_fvar
InvBoxCoxargument. Optional parameter required if biasadj=TRUE. Can either be the forecast variance, or a list containing the interval level, and the corresponding upper and lower intervals.- allow_parallel
If a parallel backend is loaded and available, should the function use it?
- calibrate
Logical. If TRUE, performs rolling-origin calibration to compute horizon-specific conformal prediction intervals. This produces properly calibrated intervals that widen with forecast horizon (trumpet shape). Default is TRUE.
- calibration_horizon
Maximum forecast horizon for calibration. If NULL (default), uses
2 * frequency(y)for seasonal data or 10 for non-seasonal data.- n_cal_windows
Number of rolling windows for calibration. If NULL (default), automatically determined based on data length (max 50).
- ...
Ignored.
Value
A list class of forecast containing the following elemets
x : The input time series
method : The name of the forecasting method as a character string
mean : Point forecasts as a time series
lower : Lower limits for prediction intervals
upper : Upper limits for prediction intervals
level : The confidence values associated with the prediction intervals
model : A list containing information about the fitted model
newx : A matrix containing regressors
calibration : Horizon-specific conformal calibration scores (if calibrate=TRUE)
Examples
library(caretForecast)
train_data <- window(AirPassengers, end = c(1959, 12))
test <- window(AirPassengers, start = c(1960, 1))
ARml(train_data, caret_method = "lm", max_lag = 12) -> fit
#> initial_window = NULL. Setting initial_window = 112
#> Loading required package: ggplot2
#> Loading required package: lattice
#> + Training112: intercept=TRUE
#> - Training112: intercept=TRUE
#> + Training113: intercept=TRUE
#> - Training113: intercept=TRUE
#> + Training114: intercept=TRUE
#> - Training114: intercept=TRUE
#> + Training115: intercept=TRUE
#> - Training115: intercept=TRUE
#> + Training116: intercept=TRUE
#> - Training116: intercept=TRUE
#> Aggregating results
#> Fitting final model on full training set
#> Performing horizon-specific calibration for conformal prediction intervals...
#> Calibrating conformal scores using 34 rolling windows...
#> Calibration complete. Samples per horizon: 34 to 34
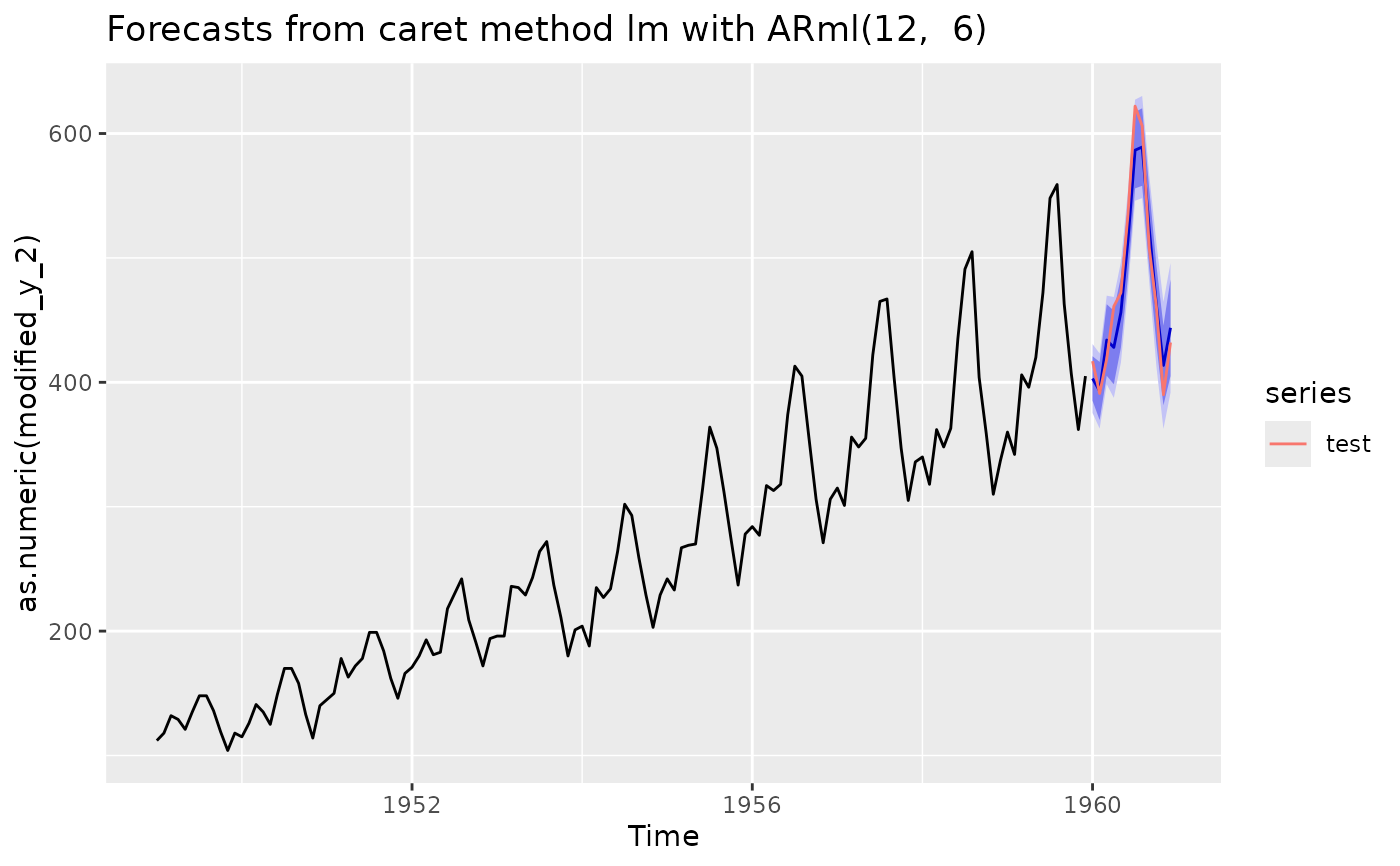
forecast(fit, h = length(test)) -> fc
autoplot(fc) + autolayer(test)
 accuracy(fc, test)
#> ME RMSE MAE MPE MAPE MASE
#> Training set -6.039671e-15 10.19861 7.884296 -0.1380603 3.263387 0.2589260
#> Test set 5.515070e+00 19.71858 17.108979 0.8260714 3.540353 0.5618712
#> ACF1 Theil's U
#> Training set 0.07296876 NA
#> Test set 0.32299513 0.3864957
accuracy(fc, test)
#> ME RMSE MAE MPE MAPE MASE
#> Training set -6.039671e-15 10.19861 7.884296 -0.1380603 3.263387 0.2589260
#> Test set 5.515070e+00 19.71858 17.108979 0.8260714 3.540353 0.5618712
#> ACF1 Theil's U
#> Training set 0.07296876 NA
#> Test set 0.32299513 0.3864957
